Types Of Computers and Their Functions
Table of Contents
Want to know What is a Computer? How Many Types of Computer? A computer is a programmable electronic device that evaluates data according to a set of commands, produce output as a result and store it for future use. Important types of computers are Personal Computers, Micro Computers, Minicomputers (Midrange Computers), Mainframe Computers, Super Computers, Servers, Workstations, Embedded Computers, Desktop Computers, Hybrid Computers.
Personal Computers, Microcomputers, Desktop Computers, Hybrid computers, etc.
Do You Know About:
What is a Computer?
Definition: A computer is an Electronic device that is designed & programmed to take raw information from the user and converts it into processed and understandable information.

For example, when we write some text, information is sent to the computer by the keyboard and the result is displayed to us via a monitor. Computers are very fast in speed and can perform very high mathematical calculations in seconds.
How does a Computer System Work?
A computer works in 4 basic steps:
- Input
- Process
- Output
- Storage
Let us now understand what is input, process, and output.
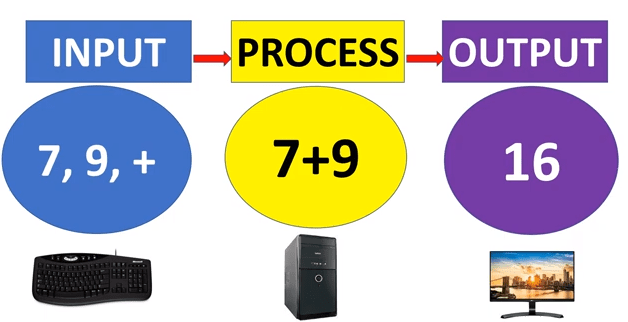
Input
The data and information that we enter into the computer are called Input. Data means letters, numbers, pictures, or any instructions. We input data using a keyboard or a mouse.
Process
The process is done by the CPU. Process means doing some work on the data that we have entered. The CPU does all the thinking and calculations with the data given. The CPU is called the brain of the computer.
Output
Output means the final result when the CPU finishes processing the data. The output is displayed on the monitor. Monitor and Printer are the most common output devices.
Storage
Storage means saving the data & information. A Computer system has different storage devices that are used to store data permanently. This data can also be retrieved as and when required.
Furthermore, A computer has the power to perform complex and repetitive tasks more quickly, precisely, and reliably. Modern computer systems are electronic and digitalized. The actual parts like wires, screens, system units, and circuits are called hardware.
The set of commands that are used to operate a computer system is called software. Click on the below button to explore all general-purpose computers hardware components:
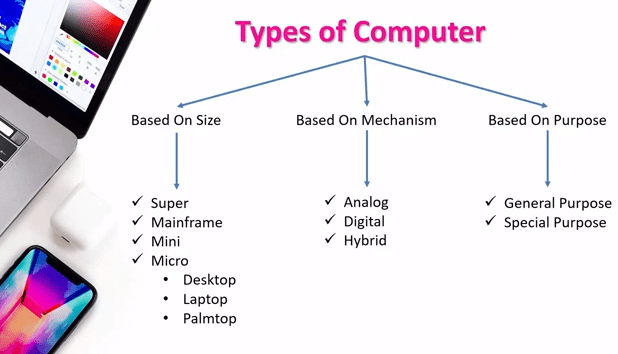
What are the 10 Types Of Computer?
A computer is a combination of software and hardware. Computers are available in multiple shapes and sizes. There are many types of computers that are classified on the basis of their function, usage, capacity, speed, reliability, power, and purpose. Here is the list of different types of computers and their functions:
Personal Computer: It is a small, single-user computer system with a microprocessor.
Workstation: It is a powerful, single-user computer. A workstation is similar to a personal computer, but it has a more powerful microprocessor than a personal computer with a higher-quality monitor.
Minicomputer: It is a multi-user computer that has the power to provide services to about a hundred users at the same time.
Mainframe: A more powerful multi-user computer than a Minicomputer. it is capable of supporting hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously.
Supercomputer: An extremely powerful and fast computer that can perform billions of instructions in a single second.
Personal Computers
The personal computer can perform input, output, processing, and storage activities by itself. It consists of input & output devices, storage devices, memory, and processor. It may consist of single or multiple processors. Commonly used personal computers are PC and Apple Macintosh.

Furthermore, personal computers have different processors and operating systems. The PC and its compatible computers use Windows operating systems. Apple Macintosh and its compatible computers use the Macintosh operating system also called Mac OS.
The PC and its compatible computers follow the specifications of the original IBM personal computer. Some PC-compatible computers include Compaq, Dell, and Toshiba.
Micro Computer
The microcomputer was invented in the 1970s. Its basic purpose is to perform home computing and dedicated data processing. This type of computer can process data and information. So advanced in technology have improved microcomputer capacities resulted in the explosive growth of personal computers in industry.

So in 1980, many medium or small design firms were finally introduced which results in the low cost and availability of microcomputers. After this time, it becomes possible for all the companies & industries to use this microcomputer because of its low cost.
Microcomputers can be divided into three types:
- Desktop
- Laptop
- Palmtop
Workstations
A workstation is a computer designed for individual use that is very fast and more efficient than a personal computer. A typical workstation computer is usually configured with some version of networking software, network interface card, and the necessary cables.

File servers are used to save files that why these types of computers do not necessarily need large storage hard drives Almost any computer can serve as a network workstation. Any computer on a network can serve as a network workstation. Such workstations are also called network clients.
Mini Computers (Midrange Computers)
A minicomputer is a medium-sized fully functional powerful computer designed to serve multiple users simultaneously.

Minicomputers are machines known as “Midrange Servers” used by small businesses and firms. A minicomputer has less processing and data storage capabilities than super and mainframe computers.
Mainframe Computer
A mainframe computer is a large, powerful, and expensive computer that can tackle thousands of clients or users at the same time. Mainframe computers are used by huge firms, organizations, and industries to handle a huge volume of data, instructions, and information.
Clients use terminals to get connected to a mainframe computer. A terminal is a device that has just a keyboard and screen. The user uses the terminal to put input to the computer and receive the result as an output on the screen. The terminal itself has no processing and storage capabilities.
Super Computer
A supercomputer is an extremely fast computer with the fastest speed and huge memory that can perform billions of instructions per second. A supercomputer costs about 30 M+ dollars. The first supercomputer “CDC6600” was designed by Seymour Cray in 1964.

Supercomputers refer to the class of most powerful computer systems that are used to do high-profile jobs like weather forecasting, genetic analysis, and code-breaking that need many calculations.
Servers
A server is a computer with the ability to provide services to other computer programs and their users connected to it through a network. Servers are physical computers dedicated to performing some computational tasks on behalf of clients. Important types of servers are:
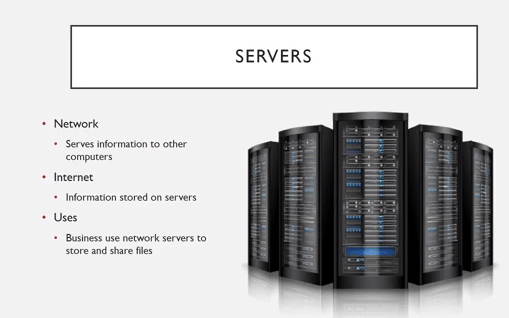
- Database Server
- File Server
- Mail Server
- Print server
- Web Server
- Gaming Server
5 Types Of Desktop Computer System
A desktop computer is designed in a way that all its components fit on a desk or table. Desktop computers are based on a system unit that manages and controls all computer operations and peripheral devices like input, output, storage, and communication devices connected with it.
Desktop Model
In this model, the table holds the system unit horizontally and a monitor is placed on the system unit.
Tower Model

The other one is the tower model. In the tower model, the table holds both the monitor and the system unit. In the tower model, the system unit is vertical.
Desktop computers are available at a low price. These types of computers are mostly used for building a network inside an organization, institute, or industry
Notebook or Laptop Computer
A notebook computer normally known as the laptop is a small portable briefcase-sized device with a small screen i.e LED or LCD and keyboard. It is an extremely light-weight & powerful computer than a PC. Notebook computers typically weigh less than 6 pounds (2- 2.5 kg).
It has the same approach as a personal computer with all applications but portable in nature. When we are working in a mobile computing environment, a notebook computer is the best replacement for a PC.
Tablet Computer

A tablet computer or tablet is a mobile computer with a touch screen interface, battery, and circuits mounted in a single unit. A tablet computer is normally equipped with all cell phone functions like calling or wireless internet & sensors including cameras, microphones, and finger or stylus gestures.
PDA Computer
PDA is the abbreviation of the personal digital assistant. It is a handheld computer with a small display of use stylus to operate. PDA works as a personal information manager that synchronizes with a desktop computer to give access to contacts, address book, notes, email, and other features.
Smartphones
Using smartphones, you can make phone calls, access the Internet, manage contact information, send emails and text messages, play games, and take pictures. These phones usually don’t have keyboards and large screens.
Embedded Computer
Embedded computers are defined as special-purpose systems in which the computer is completely embedded inside the device it controls. An embedded system performs pre-defined tasks or a few dedicated functions. In general, it does not provide programmability to users like PC.
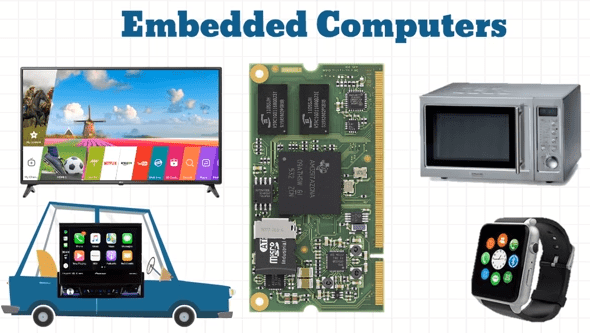
Embedded systems directly control some hardware. Embedded systems are an important part of our daily life. Microwave ovens, MP3 Players, traffic signals are very common embedded systems in our life.
Hybrid Computer
A hybrid computer is a type of computer system that combines the features of analog computers and digital computers Hybrid computers help the user to exploit the desirable features of the machines to process both continuous and discrete data. It can also accept data in both analog and digital forms.
Logical operations are handled by digital components while the differential equations are normally performed by analog components. Hybrid computers are used in hospitals to measure and monitor the heartbeat of the patient and the devices used at petrol pumps for fuel refilling.
A hybrid computer is a combination of both an analog and a digital computer. Some part of the processing is done on an analog computer and some part of a digital computer. A hybrid computer joins the top characteristics of both analog and digital computers.
Examples of Hybrid Computer
We can use hybrid computer devices to examine the patient’s heart function, temperature, blood pressure, and other signs. This measurement may then be converted into numbers and displayed in digital form.

