Types Of Organization And Its Characteristics
Table of Contents
An organization is a social unit of people scientifically structured and managed to meet a need or to chase joint goals on a long-term basis. A Computer system must be an essential part of any organization.
This comprehensive article is all about the basic concept of an organization, basic principles, its types, and important characteristics. So don’t wait and read this knowledgeable article.
Concept of Organization
A social unit of people scientifically structured and managed to meet a need or to chase joint goals on a long-term basis using different communication devices.
All organizations have a management structure that determines the relationship between functions and positions and subdivides and delegates roles, responsibilities, and authority to carry out defined tasks.
Organizations are open systems in that they influence and are affected by the environment away from their boundaries.
Do You Know About:
- Psfont tk APK [Fancy Font Generator]
- Fyptt APK
- Watch Online Movie Apk
- Multithreading And Its Models
- Interprocess Communication In OS
- Four Conditions For Deadlock
- Types of System Call With Their Functions
Definition:
It includes both structures of the machinery and the process. An organization, as a structure, is a pattern of relationships.
It is the positioning of the workers through whom effort will flow i.e. the assignment of duties and responsibilities. The coordination and integration of activities of all the persons engaged in the pursuit, the tool for attaining the objectives.
A person, paces, and things have to be so arranged that effort flow freely towards the desired goals, and this is the process of organizing. As a process organizing means directing and controlling the relationships between persons and persons and between persons and their work.
Basic Principles
- It should not be static; the organization needs continuous reorganization.
- It should be flexible so as to improve both relationships and standards of efficiency.
- A good organization should be modified as and when education theory advances, bringing in curricula should be brought about slowly and with consultation and consent.
- It should provide for participation in policymaking and other administrative activities by teachers, students, parents, and the community. Participation broadens and strengthens human relationships.
- Organizational charts detailing “functions, jurisdictions, responsibilities, relationship, limits of authority, objectives, and methods of measuring performance, etc.” promote better understanding and larger output.
Structure Of Organization
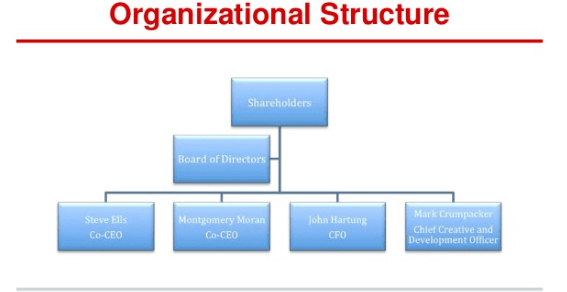
Types of Organization
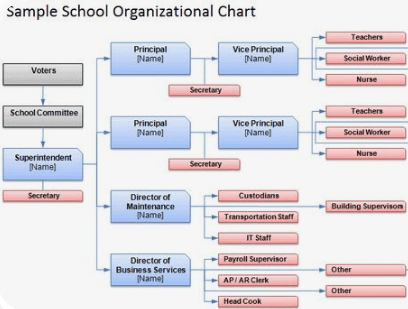
School Organization
“Organization of a school is the administrative phase of educational theory.” (Elsbree). Dewey. “The school is a unique environment where a certain quality of life and a certain type of activities and occupations are provided with the purpose of securing a child’s development along desirable lines.”
Formal Organization
It is established by law and custom and the informal is the man-to-man relationship. The formal is concerned with positions, the information with people. Both of these are essential and interrelated. All individuals in the formal organization have their parallel roles in the informal.
Informal Organization
It is the human factor and relates to the reaction of persons to each other and to the activity. A good administrator established both formal and informal organizations.
He should set up the formal in keeping with the requirements of the task and also develop informal to reinforce efforts and activities. It should be democratic, i.e., based on personal relationships, willing cooperation, and active participation of all the persons involved.
If power and control are not concentrated at the top but shared by all through actual participation, people are brought nearer together and effort integrated. In a good organization, impetus and initiative for action come from the people themselves and are not imposed from above.
Characteristics Of Organization
Curriculum, Instruction, and Assessment
Educators value young adolescents and are prepared to teach them. Students and teachers are engaged in active, Purposeful learning. The curriculum is challenging. Exploratory, integrative, and relevant.
Educator uses multiple learning and teaching approaches. diverse and current assessments advance learning as well as calculate it.
Leadership and Organization
A common vision developed by all stakeholders guides every judgment. Leaders are devoted to and familiar with this age group. Leaders express courage and association.
Culture and Community
The school environment is appealing, harmless, inclusive, and helpful of all. Every student’s educational and private development is guided by an adult activist. Comprehensive direction and support services meet the desires of young youth.
Health and wellness are supported in the curriculum, school-wide programs, and associated policies. The school aggressively involves families in the education of their children. The school includes society and business partners.



