Data Transmission Modes in Computer Network
Table of Contents
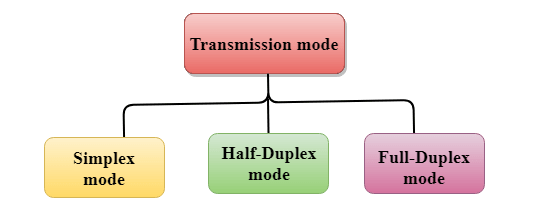
Transmission mode defines the direction of the flow of data between two communication devices connected over a network. Simplex, Half Duplex, and Full Duplex are major types of data transmission modes. It is also known as data communication mode or directional mode.
What is Data Transfer?
Data transfer is a process of the collection, duplication, and transfer of large data sets from one organization or business unit to another. Data transfer uses various transmission means to transfer information from one place to another.
For example, when we open a web page, all text, images, and other data are transferred to the computer by means of the Internet.

We can say that data transfer is a technique of using computational procedures and technologies to transfer electronic or analog data from one computer to another. Data is transmitted in the form of bits and bytes on a digital or analog medium.
Read About:
Types Of Computers and Their Functions
Central Processing Unit
Wwxxyyzz 2020 Xbox 360 APK
What is Data Transmission Mode?
The data transmission mode is a method of specifying the direction of data flow between two devices connected over a network for data and information sharing. A data transmission mode identifies the direction of data flow from one device to another in a network.
The method of transferring data from one device to a different one is called transfer mode. The transmission mode is additionally referred to as the communication mode.
Each channel features a direction with which it communicates and provides the transmitting media. Therefore, the transfer mode is additionally referred to as the directional mode. The transmission mode is defined within the physical layer.
Data Transfer Modes Based On Coordination
Data transfer modes based on coordination between sender and receiver are:
- Synchronous
- Asynchronous
Synchronous
In synchronous data transmission mode, the data bits are transmitted one by one, without interruption. The start and end bits define the beginning and end of each frame or block of data. While they have an advantage, they slow down the data transmission somewhat.
In synchronous data transfer, both the sender and receiver synchronize their working speed according to the same system clock. Bytes are sent as connected bit blocks, and since the blocks have no start or stop bits. The message node must sort them in the correct order after the bits are received.
Asynchronous
Asynchronous data transmission in N mode bit messages sent at the start and stop. The start and stop bits ensure the correct transmission of data from the sender to the recipient. In total, the start bit is 0 and the stop bit is 1.
The speed of the sender and the recipient are not synchronized, so messages are sent at irregular intervals and only one byte of data can be sent at a time. This type of data transmission is best suited for short distances.
Data Transfer Modes In A Network
Data transfer modes are based on the number of communication paths or the number of bits that are sent simultaneously on a network Data is transmitted through serial and in parallel ways; We will explain each case below.
- Serial Transfer
- Parallel Transmission
Serial Transfer
In this method, the data moves just like a narrow two-way street where cars are moving one after the other, the bits are moved one after the other in a row. For example, data is transmitted serially over telephone lines.
Parallel Transmission
In this method, data travels just like a one-way multi-lane highway where several cars are moving together and on different lanes of the highway. All the data is transmitted in the form of bits through several lines in parallel and simultaneously. This method is used for short distances such as connecting a computer to a printer.
Data Transfer Modes in Data Exchange
The physical layer of the Open System Interconnection(OSI) Layer Model decides how the data is transmitted in a network. Its main function is to specify the direction of data flow through which the data travel to reach the receiver or node. Three main types of data transmission modes are:
- Simplex Mode
- Half-Duplex Mode
- Full-Duplex Mode
Simplex Mode
Simplex is the data transmission mode in which the data transmission is unidirectional, only in one direction. When two devices are linked in simplex mode only the sender device can send data while the receiver only receives data. It cannot be transmitted in both directions.
This mode of transmission isn’t very fashionable because communications require two-way data exchange. Simplex mode is employed in commercial contexts like sales that don’t require a corresponding response.
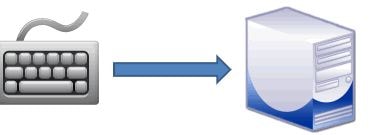
The station may be a Simplex channel because it transmits the signal to the listeners but never allows them to return. The keyboard and monitor are samples of simplex mode because the keyboard can only accept data from the user and therefore the monitor is merely wont to display data on the screen.
The main advantage of the Simplex mode is that you simply can use the complete capacity of the channel during transmission.
In simplex mode, data moves only in one direction similar to a one-way street. The direction of flow never changes. In simplex mode, a device just only sends or receives data. It cannot be able to perform both actions. Examples of Simplex modes are Radio and TV transmission, keyboard, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Simplex Data Transmission Modes
| Advantages | Dis-Advantages |
| Enquire full capacity of the channel during data transmission | Don’t support two-way communication |
| Low chances of data traffic issues | No mechanism to transmit information back to the sender |
Half-Duplex Mode
The half-duplex mode enables the flow of data in both directions but not at the same time. Data can flow in one direction at one time. In other words, each device in a link can transmit and receive the data but not at the same time.
The total bandwidth of the channel is employed directly in one direction. In Half-duplex mode, error detection is feasible, and within the event of a mistake, the receiver asks the sender to retransmit the info.
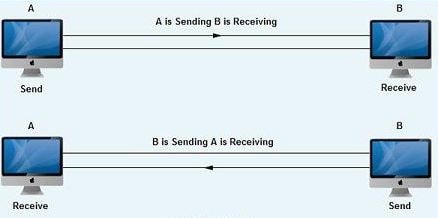
The speed of the half-duplex mode is slow. An example of half-duplex communication is internet surfing where there is no need for communication in both directions at the same time. The user enters a command in order to request a web page. The web page is downloaded and displayed before the user.
Police radios are an example of a half-duplex mode. On police radios, one person speaks, and another listens. After the pause, another speaks and therefore the first party listens. Talking at an equivalent time creates a distorted sound that’s not understood.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Half-Duplex Data Transmission Modes
|
Advantages |
Dis-Advantages |
| It optimizes the full capacity of the transmission channel | May occur a delay in transmission due to one-way communication at a time. |
| Enables two-way communication | Two-way communication but not at the same time |
Full-Duplex Mode
Full-Duplex is the data communication mode in which the data can travel in both directions simultaneously. The full-duplex mode is a faster way of data transmission as it is bi-directional in nature. Time is not wasted in changing the direction of data flow.
Full-duplex mode has two Simplex channels. One channel has traffic following in one direction and another channel has traffic flowing within the other way. Full-duplex mode is the fastest mode of communication between devices.
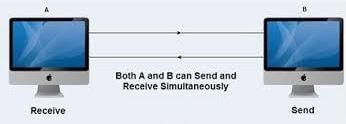
The common example of Full-duplex mode is the telephone network. When two people are communicating with one another over a telephone line, they will both talk and listen at an equivalent time.
The bandwidth of the full-duplex mode is double as compared to the half-duplex. In this communication mode, the capacity of channels is divided between two directions. An example of full-duplex mode is a Telephone Network, in which both persons can talk and listen to each other at the same time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Full-Duplex Data Transmission Modes
| Advantages |
Dis-Advantages |
| Two-way communication at the same time | No dedicated path exists because the communication channel divided into two parts |
| Faster than Half-Duplex mode | Improper utilization of channel bandwidth as there exist two separate paths |